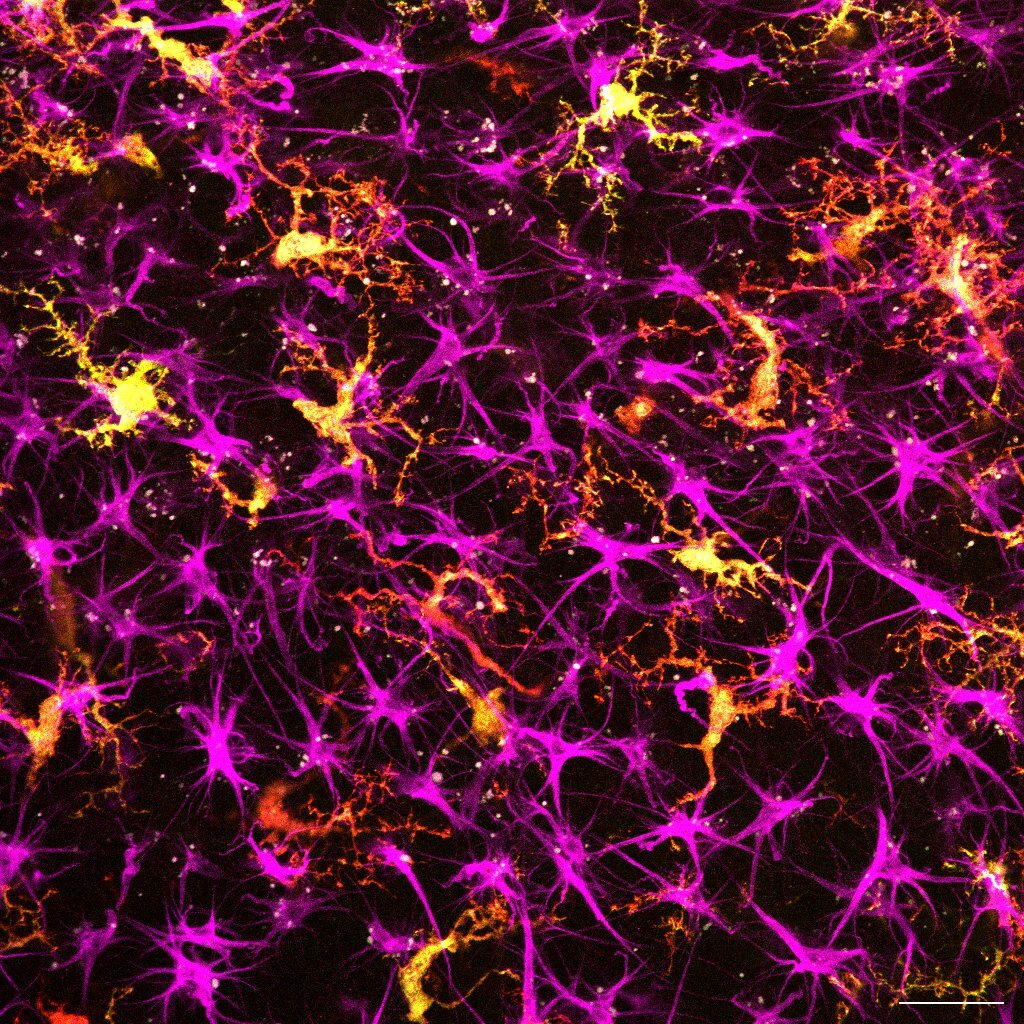
In our recent study we examined the role of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) in synaptic plasticity. Using mouse organotypic tissue cultures, we found that TNFα influences both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, we discovered that pro-inflammatory microglia play a crucial role in mediating negative feedback mechanisms in the context of TNFα-induced synaptic plasticity, thus supporting synaptic homeostasis. These findings emphasize microglia’s importance as gatekeepers of synaptic change and stability.
Click here to get to the full article!